
In the previous article , we discussed 10 Very Short Answer Type Questions. In this article, we will discuss few more VSA type Questions from Chhaya Mathematics , Class 11 (S N De book ).
Circle related Problems and Solutions | S N Dey Mathematics
11. The co-ordinates of the centre of the circle ![]() are
are ![]() ; find
; find ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution.
The given equation of the circle can be rewritten as :
![]()
Now, comparing the equation ![]() with the general / standard form of circle
with the general / standard form of circle ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
So, the centre of the circle as represented by ![]() is :
is :
![]()
By ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
- To download full PDF solution of Circle ( Chhaya Mathematics, Class 11 ), click here.
12. Find the equation of the circle which touches both the co-ordinate axes at a distance ![]() unit from the origin.
unit from the origin.
Solution.
From the given condition, we can say that the centre of the circle is ![]() and the radius of the circle is
and the radius of the circle is ![]() unit so that the equation of the circle can be written as :
unit so that the equation of the circle can be written as :
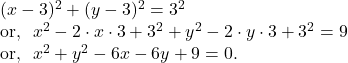
13. Find the parametric equation of the circle ![]()
Solution.
We have, ![]()
Comparing the equation ![]() with the general / standard form of circle
with the general / standard form of circle ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
The centre of the given circle is : ![]()
The radius of the circle :
![]()
Hence, the equation of the circle is :
![]()
By ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
The equations ![]() together represent the parametric equation of the circle.
together represent the parametric equation of the circle.
14. The parametric equation of a circle are, ![]() Find the equation of the circle.
Find the equation of the circle.
Solution.
We have,
![]()
![]()
Hence, from ![]() we get,
we get,
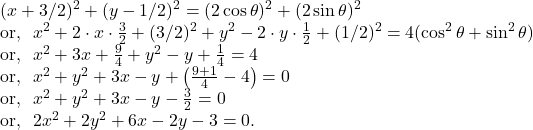
15. The equation of the in-circle of an equilateral triangle is ![]() find the area of the equilateral triangle.
find the area of the equilateral triangle.
Solution.
The equation of the in-circle of an equilateral triangle is given by ![]()
Comparing the equation ![]() with the general / standard form of circle
with the general / standard form of circle ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
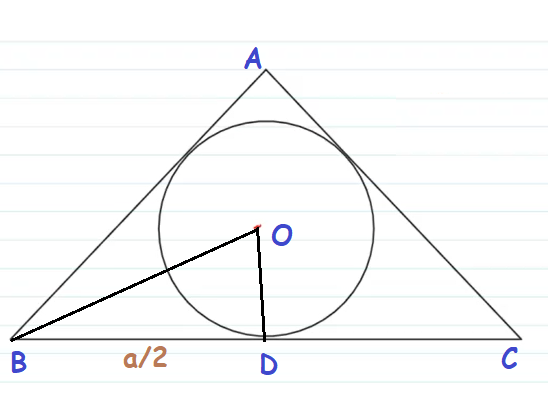
The radius of the circle is :
![]()
Clearly, from the figure we notice that ![]() Now let
Now let ![]() so that
so that ![]()
