In the previous article , we solved few solutions of Short Answer Type Questions of Ellipse Chapter of S.N.Dey mathematics, Class 11. In this chapter, we will solve few more.

4(i) Find the lengths of axes of the ellipse whose eccentricity is ![]() and the distance between focus and directrix is
and the distance between focus and directrix is ![]()
Solution.
The distance between focus and directrix ![]()
By question,


Hence, the length of the major axis ![]() and the length of the minor axis
and the length of the minor axis ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are two foci of an ellipse whose eccentricity is
are two foci of an ellipse whose eccentricity is ![]() Find the length of the major axis.
Find the length of the major axis.
Solution.
Eccentricity ![]()
The distance between the two given foci is

Hence, the length of the major axis ![]()
5. The length of the latus rectum of an ellipse is ![]() unit and that of the major axis, which lies along the
unit and that of the major axis, which lies along the ![]() axis , is
axis , is ![]() unit. Find its equation in the standard form . Determine the co-ordinates of the foci and the equations of its directrices.
unit. Find its equation in the standard form . Determine the co-ordinates of the foci and the equations of its directrices.
Solution.
The length of the latus rectum of the ellipse is given by
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{2b^2}{a}=8 \\ \text{or,}~~ b^2=4a=4 \times 9 ~~[\because ~2a=18] \\ \therefore~ b^2=36.](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7059a402069855e9738492344516d931_l3.png)
Again, the length of the major axis (2a) is given by
![]()
Hence,the equation of the ellipse is
![]()
The eccentricity ![]() of the ellipse is given by
of the ellipse is given by

The co-ordinates of the foci of the ellipse is given by
![]()
The equation of the directrix is given by
![]()
6. Taking major and minor axes along ![]() and
and ![]() axes, find the equation of the ellipse whose
axes, find the equation of the ellipse whose
![]() co-ordinates of foci are
co-ordinates of foci are ![]() and the length of minor axis is
and the length of minor axis is ![]()
Solution.
Since the foci of the given ellipse lie on the ![]() -axis , the major axis of the ellipse lies on the
-axis , the major axis of the ellipse lies on the ![]() axis.
axis.
Again, the centre of the ellipse is given by ![]() i.e.
i.e.![]()
So, the ellipse is of the form ![]()
So, the co-ordinates of the foci ![]()
The length of the minor axis is given by
![]()

Hence, using ![]() , the equation of the ellipse is
, the equation of the ellipse is
![]()
![]() eccentricity
eccentricity ![]() and the length of latus rectum
and the length of latus rectum ![]()
Solution.

Length of latus rectum

From ![]() and
and ![]() we get,
we get,
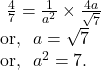
So, the equation of the ellipse is

![]() length of minor axis is
length of minor axis is ![]() and the distance between the foci is
and the distance between the foci is ![]()
Solution.
By the condition, length of minor axis ![]() is given by
is given by
![]()
The distance between the foci is

Hence, the equation of the ellipse is given by

![]() co-ordinates of one vertex are
co-ordinates of one vertex are ![]() and the co-ordinates of one end of minor axis are
and the co-ordinates of one end of minor axis are ![]()
Solution.
By question, the equation of the ellipse can be taken as ![]()
Co-ordinates of one vertex is ![]() and co-ordinates of one end of minor axis is
and co-ordinates of one end of minor axis is ![]()
![]()
Hence, by ![]() we get,
we get,

![]() co-ordinates of foci are
co-ordinates of foci are ![]() and the eccentricity is
and the eccentricity is ![]()
Solution.
By question, the co-ordinates of foci ![]()

![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com ~a^2e^2=8^2~~[\text{By (1)}] \\ \text{or,}~~ a^2\left(1-\frac{b^2}{a^2}\right)=64\\ \text{or,}~~ a^2-b^2=64 \\ \text{or,}~~ 10^2-b^2=64 \\ \text{or,}~~ b^2=100-64=36](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0661eb5bf59a3cb42527428700976658_l3.png)
Hence, the equation of the ellipse is

![]() Find the equation of the ellipse whose
Find the equation of the ellipse whose
![]() eccentricity is
eccentricity is ![]() focus is
focus is ![]() and directrix is
and directrix is ![]()
Solution.
Let ![]() be any point on the ellipse . The co-ordinates of the focus :
be any point on the ellipse . The co-ordinates of the focus : ![]() and the equation of the directrix is given by
and the equation of the directrix is given by ![]()
Now, the length of the perpendicular from P on the straight line (1) is given by
![]() ,
,
![]()
Now, for the ellipse, we have

Hence, the equation of the ellipse is given by ![]()
![]() eccentricity is
eccentricity is ![]() focus is
focus is ![]() and directrix is
and directrix is ![]()
Solution.
Let ![]() be any point on the ellipse. The co-ordinates of the focus :
be any point on the ellipse. The co-ordinates of the focus : ![]()
The equation of the directrix is ![]()
The length of the perpendicular from P on the straight line (1) is
![]() ,
,
![]()
Now, for the ellipse
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{SP}{PM}=e=\frac{\sqrt{7}}{4}~\text{(given)} \\ \text{or,}~~ \frac{SP^2}{PM^2}=\frac{7}{16} \\ \text{or,}~~ 16 SP^2=7PM^2 \\ \text{or,}~~ 16[x^2+(y+\sqrt{7})^2]=7 \times \frac{(\sqrt{7}y+16)^2}{7} \\ \text{or,}~~ 16x^2+16(y^2+2\sqrt{7}y+7)=7y^2+2\sqrt{7}y \times 16 +16^2 \\ \text{or,}~~ 16x^2+16y^2+32\sqrt{7}y+112=7y^2+32\sqrt{7}y+256 \\ \text{or,}~~ 16x^2+9y^2=144.](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cc4d307c49503252443fa9379280b5f8_l3.png)
Hence, the equation of the ellipse is ![]()
![]() eccentricity is
eccentricity is ![]() focus is
focus is ![]() directrix is
directrix is ![]()
Solution.
Let ![]() be any point on the ellipse. The co-ordinates of focus :
be any point on the ellipse. The co-ordinates of focus : ![]() The equation of the directrix :
The equation of the directrix : ![]()
The perpendicular distance of the point P from the straight line (1) is
![]()
![]()
Now, for the ellipse, we know that
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{SP}{PM}=e=\frac 12~~\text{(Given)} \\ \text{or,}~~ SP^2=\left(\frac 12\right)^2 PM^2 \\ \text{or,}~~ 4[(x+1)^2+(y-1)^2]=\frac 12(x-y+3)^2 \\ \text{or,}~~ 8(x^2+2x+1)+8(y^2-2y+1)=(x-y)^2+2(x-y) \cdot 3+3^2 \\ \text{or,}~~ 8x^2+16x+8+8y^2-16y+8=x^2+y^2-2xy+6x-6y+9 \\ \text{or,}~~ 7x^2+7y^2+2xy+10x-10y+7=0.](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c38745c19f06bf55447fe8c323ddcbfd_l3.png)
![]() focus is
focus is ![]() directrix is
directrix is ![]() and eccentricity is
and eccentricity is ![]()
Solution.
Let ![]() be any point on the ellipse. The co-ordinates of focus :
be any point on the ellipse. The co-ordinates of focus : ![]() The equation of the directrix :
The equation of the directrix : ![]()
The perpendicular distance of the point P from the straight line (1) is
![]()
Now, for the ellipse, we know that
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{SP}{PM}=e=\frac 23~~[\text{given}] \\ \text{or,}~~ SP^2=\frac 49 PM^2 \\ \text{or,}~~9[(x-3)^2+(y-4)^2]=\frac{4(3x+4y-5)^2}{25} \\ \text{or,}~~ 225(x^2-6x+9+y^2-8y+16)=4(9x^2+16y^2+25+24xy-40y-30x) \\ \text{or,}~~ 189x^2-96xy+161y^2-1230x-1640y+5525=0\rightarrow(2)](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b12a14e29b1c1ac846493025b7a7efee_l3.png)
Hence, the equation ![]() represents the required ellipse.
represents the required ellipse.