In the previous article , we have solved few VSA type questions of Hyperbola chapter of S.N.Dey mathematics, Class 11. In this article , we will solve few Short Answer Type questions of Hyperbola related problems of s n dey mathematics class 11.

1. Find (i) the length of axes (ii) length of latus rectum (iii) co-ordinates of vertices (iv) eccentricity (v) co-ordinates of foci and (vi) equations of the directrices of each of the following hyperbolas :
![]()
Solution (a)

Comparing ![]() with the general equation of hyperbola
with the general equation of hyperbola ![]() we get,
we get, ![]()
(i) The length of the transverse axis ![]() and the length of the conjugate axis
and the length of the conjugate axis ![]()
(ii) The length of latus rectum
![]()
(iii) The co-ordinates of vertices: ![]()
(iv) Eccentricity ![]()
(v) The co-ordinates of the foci :
![]()
(vi) Equations of directrices are

Solution(b)
![]()
Comparing ![]() with the general equation of hyperbola
with the general equation of hyperbola ![]() we get,
we get, ![]()
(i) The length of the transverse axis ![]() and the length of the conjugate axis
and the length of the conjugate axis ![]()
(ii) The length of latus rectum
![]()
(iii) The co-ordinates of vertices: ![]()
(iv) Eccentricity ![]()
(v) The co-ordinates of the foci :
![]()
(vi) Equations of directrices are
![]()
2. Find the length of the transverse and conjugate axes of the hyperbola ![]() Write down the equation of the hyperbola conjugate to it and find the eccentricities of both the hyperbolas.
Write down the equation of the hyperbola conjugate to it and find the eccentricities of both the hyperbolas.
Solution.
![]()
Comparing ![]() with the general equation of hyperbola
with the general equation of hyperbola ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
So, the length of the transverse axis ![]() and the length of the conjugate axis
and the length of the conjugate axis ![]()
2nd Part :
The equation of the conjugate hyperbola is
![]()
3rd Part :
The eccentricity ![]() of the hyperbola is
of the hyperbola is
![]()
The eccentricity ![]() of the conjugate hyperbola is
of the conjugate hyperbola is
![]()
3. Find the equation of the hyperbola, whose axes are axes of co-ordinates and
(i) length of transverse and conjugate axes are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Solution.
Since the transverse axis is along ![]() -axis and conjugate axis is along
-axis and conjugate axis is along ![]() -axis, so the equation of the hyperbola can be written in the form of
-axis, so the equation of the hyperbola can be written in the form of ![]()
So, by question,
![]()
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is
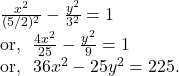
(ii) lengths of conjugate axis and latus rectum are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Solution.
By question, the length of conjugate axis ![]() and the length of latus rectum
and the length of latus rectum ![]()
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is

(iii)which passes through the points ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution.
The hyperbola ![]() passes through the points
passes through the points ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
So, from ![]() and
and ![]() we get,
we get,

So, by ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
Hence, the required equation of the hyperbola is
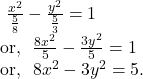
MTG 45 Years JEE Advanced Previous Years Solved Papers with Chapterwise Solutions-Physics (1978-2022), JEE Advanced PYQ for 2023 Exam Paperback
(iv) distance between the foci is ![]() and length of conjugate axis is
and length of conjugate axis is ![]()
Solution.
The length of conjugate axis ![]()
The distance between the foci

Hence, by ![]() and
and ![]() we get the required equation of hyperbola which is
we get the required equation of hyperbola which is ![]()
(v) co-ordinates of foci are ![]() and the length of latus rectum is
and the length of latus rectum is ![]()
Solution.
The co-ordinates of foci
![]()
The length of the latus rectum
![]()
From ![]() we get,
we get,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com ~a^2e^2=\left(\frac 52\right)^2 \\ \text{or,}~~ a^2\left(1+\frac{b^2}{a^2}\right)=\frac{25}{4} \\ \text{or,}~~ a^2+b^2=\frac{25}{4} \\ \text{or,}~~ a^2+\frac 98a=\frac{25}{4}~~[\text{By (2)}] \\ \text{or,}~~ 8a^2+9a=50 \\ \text{or,}~~ 8a^2+9a-50=0 \\ \text{or,}~~ 8a^2+25a-16a-50=0 \\ \text{or,}~~ a(8a+25)-2(8a+25)=0 \\ \text{or,}~~(8a+25)(a-2)=0 \\ \therefore~ a=2~~[~\because a>0]](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-eb20f90886d340aee6242f81d1465545_l3.png)
![]()
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is

(vi)distances between the foci and directrices are ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Solution.
The distance between the foci ![]()
![]()
Again, the distance between two directrices ![]()
![]()
So, by ![]() , we get
, we get

Again, by ![]() we get,
we get,
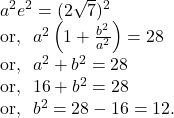
So, the equation of the hyperbola is

(vii) eccentricity is ![]() and the sum of squares of the lengths of axes is
and the sum of squares of the lengths of axes is ![]()
Solution.
By question, we have

![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com e=\frac{\sqrt{13}}{3}~~\text{(Given)} \\~~ \text{or,}~~e^2=\frac{13}{9} \\ ~~\text{or,}~~1+\frac{b^2}{a^2}=\frac{13}{9} \\~~ \text{or,}~~ \frac{a^2+b^2}{a^2}=\frac{13}{9} \\~~ \text{or,}~~ \frac{13}{a^2}=\frac{13}{9}~~[\text{By (1)}] \\ ~~\text{or,}~~ a^2=9](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c1f14fcbbe08b0b2b6426ca1ec77fb01_l3.png)
Putting the value of ![]() in
in ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is
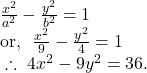
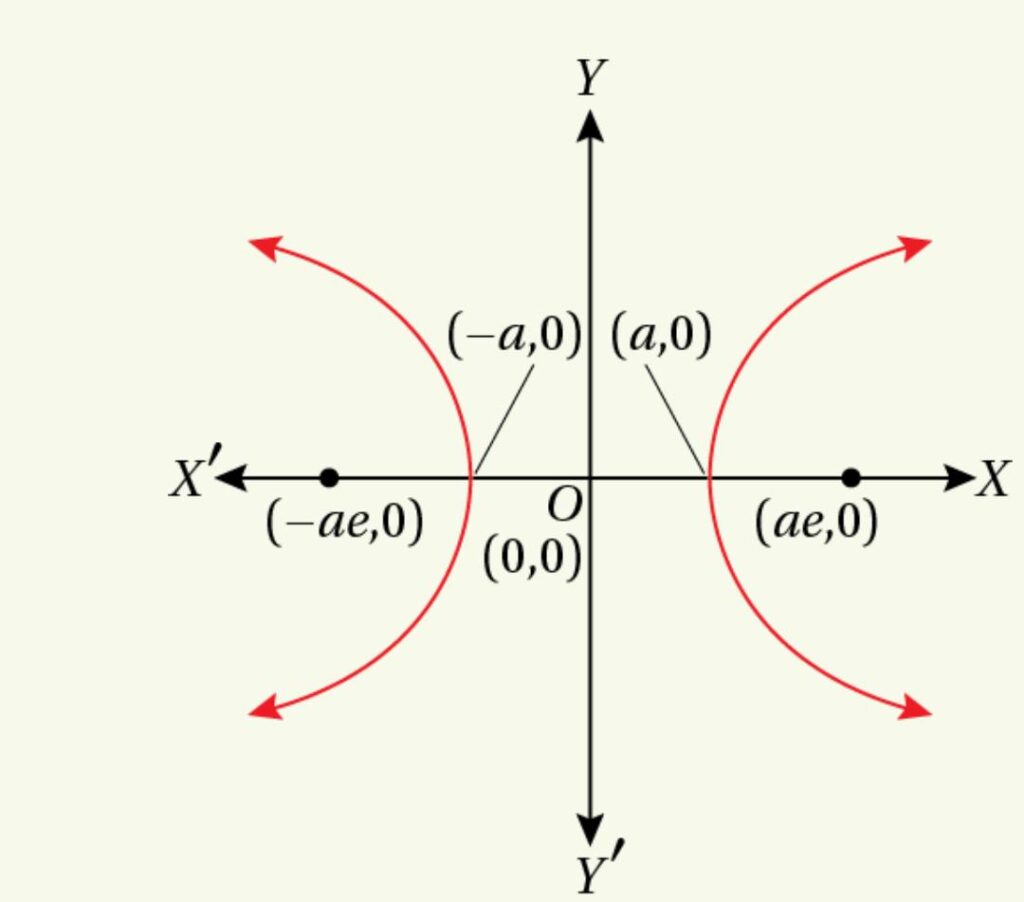
(viii)transverse axis is ![]() and the vertex bisects the line segment joining the centre and focus.
and the vertex bisects the line segment joining the centre and focus.
Solution.
Since the vertex bisects the line segment joining the centre and the focus,
![]() the distance of the vertex from the centre
the distance of the vertex from the centre
![]() (the distance of the focus from the centre)
(the distance of the focus from the centre)

Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is
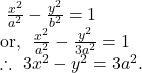
(ix) which passes through the point ![]() and whose eccentricity is
and whose eccentricity is ![]() .
.
Solution.
The hyperbola ![]() passes through the point
passes through the point ![]()

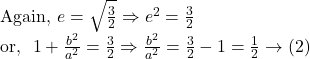
By ![]() we get,
we get,
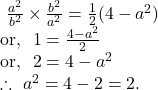
So, using ![]() we get,
we get, ![]()
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is given by

17 Year-wise JEE Advanced Previous Year Solved Papers 1 & 2 (2006 – 2022) 4th Edition | Answer Key validated with IITJEE JAB | PYQs Question Bank
(x) eccentricity is ![]() and the co-ordinates of one focus are
and the co-ordinates of one focus are ![]()
Solution.
Eccentricity ![]() is
is ![]() and the co-ordinates of one focus
and the co-ordinates of one focus ![]() are
are ![]()
![]()
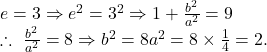
![]() The equation of the hyperbola is
The equation of the hyperbola is

(xi) eccentricity is ![]() and the length of semi latus rectum is
and the length of semi latus rectum is ![]()
Solution.
It is given that the eccentricity ![]() is
is ![]() and the length of semi-latus rectum
and the length of semi-latus rectum ![]() is
is ![]()
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com ~e=\sqrt{\frac 32} \Rightarrow e^2=\frac 32 \\ \text{or,}~~ 1+\frac{b^2}{a^2}=\frac 32 \\ \text{or,}~~ \frac{b^2}{a^2}=\frac 32-1 \\ \text{or,}~~ \frac{2a}{a^2}=\frac 12~~[\text{By (1)}] \\ \text{or,}~~ \frac 2a=\frac 12 \\ \text{or,}~~ a=4 \Rightarrow a^2=4^2=16. \\ \therefore b^2=2\times 4=8](https://examhoop.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-73ce09ebe3002eebed46d96a8455acef_l3.png)
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is
![]()
(xii)co-ordinates of foci are ![]() and the eccentricity is
and the eccentricity is ![]()
Solution.
The co-ordinates of foci ![]() and the eccentricity
and the eccentricity ![]() is
is ![]()
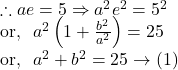

By ![]() and
and ![]() we get,
we get,
![]()
Hence, the equation of the hyperbola is


